
Why Diet is Important for Weight Loss and a Healthy Lifestyle?
In the quest for weight loss and a healthier lifestyle, many people focus primarily on exercise, often overlooking the critical role that diet plays in achieving long-term success. While physical activity is undeniably important, a balanced, nutritious diet serves as the foundation for weight management and overall well-being.
Whether your goal is to shed excess weight, maintain a healthy body, or simply feel better, understanding why diet is important and how it works can help you make smarter, more sustainable choices. This blog explores why diet is key to weight loss, how it influences your body, and how it contributes to a better lifestyle.
The Role of Diet in Weight Loss

Weight loss occurs when you burn more calories than you consume. This is known as a calorie deficit, and it’s the fundamental principle behind most weight loss strategies. While exercise can certainly help burn calories and improve fitness, diet plays a more direct and impactful role in creating this deficit. Experts agree that approximately 80% of weight loss is attributed to diet, while only 20% comes from exercise.
If you want to lose weight, the most effective approach is to control your calorie intake. For example, reducing your daily caloric intake by approximately 500 calories can lead to a weight loss of about 0.45 kg (nearly half a kilo) per week. Though this might seem small, over time it adds up to significant, sustainable weight loss. Trying to “out-exercise” a poor diet is often ineffective, as burning off excess calories through physical activity alone is difficult and exhausting.
How Diet Affects Metabolism
Diet plays a crucial role in regulating your metabolism—the process by which your body converts food into energy. Eating the right types of food in appropriate portions can help keep your metabolism active and efficient. In contrast, an unhealthy or imbalanced diet can slow down your metabolism, making it harder to lose or maintain weight.
Protein, for example, is essential for maintaining lean muscle mass. Since muscle burns more calories than fat, maintaining muscle supports a higher metabolic rate. Additionally, protein has a higher thermic effect, meaning your body uses more energy to digest and process it compared to fats and carbohydrates.
Diet and Hunger Regulation
One of the biggest hurdles in weight loss is controlling hunger and cravings. A strategic diet can help manage these better than willpower alone. Choosing the right foods keeps you fuller longer and reduces the urge to overeat.
High-protein, high-fiber, and healthy fat-rich foods help suppress hunger. Foods like chicken, fish, eggs, beans, and lentils are great sources of protein. Similarly, fiber-rich foods—including vegetables, fruits, and whole grains—slow digestion, promote satiety, and regulate blood sugar levels.
Moreover, a nutrient-rich diet helps prevent micronutrient deficiencies that can lead to cravings. For example, low levels of magnesium or iron might trigger a desire for sugary or processed snacks.
The Role of Macronutrients: Carbs, Proteins, and Fats
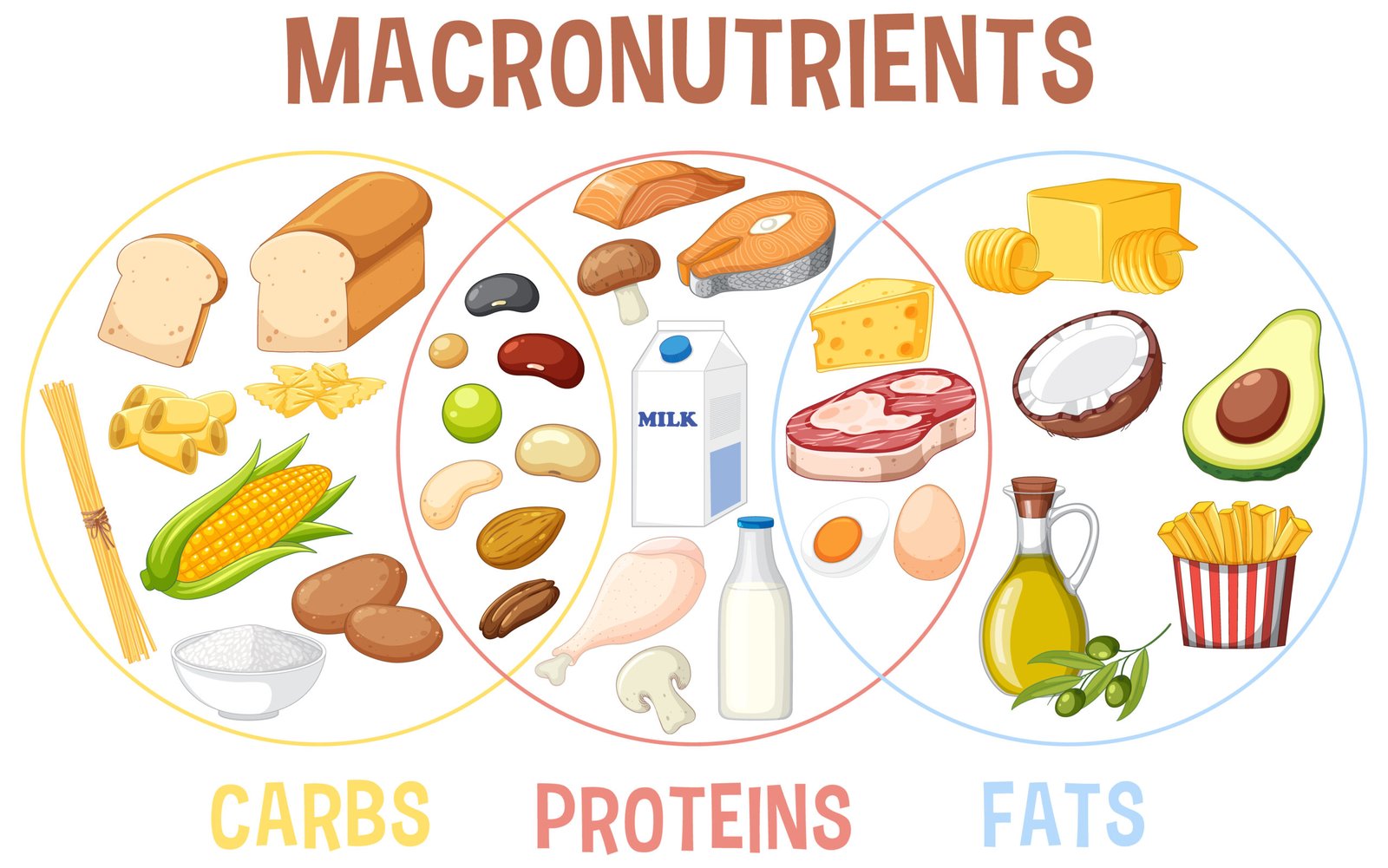
A healthy diet isn’t just about cutting calories—it’s about getting the right balance of macronutrients: carbohydrates, protein, and fats. Each of these plays an important role in the body, and understanding their function helps you make smarter dietary choices.
Carbohydrates: Fuel for the Body
Carbs are the body’s main energy source. While refined carbs (like sugary foods and white bread) can lead to weight gain, complex carbs (found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes) provide energy and fiber, support digestion, and help keep you full.
Protein: Building Blocks for a Healthy Body
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, maintaining muscle, and keeping metabolism active. When dieting, sufficient protein intake helps prevent muscle loss, which is key to long-term success. Include protein at every meal through foods like lean meats, dairy, tofu, and legumes.
Fats: Essential for Health
Despite their calorie density, healthy fats play vital roles in hormone production, brain function, and nutrient absorption. Sources include nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats to support heart health.
Sustainability and Long-Term Success
The most effective diet is one you can sustain. Fad diets and extreme restrictions might yield quick results, but often result in rebound weight gain and frustration. A long-term approach based on balance, moderation, and nourishment is the key to lasting success.
Focus on building a healthy relationship with food. Eat a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods, watch your portions, and allow flexibility. This not only supports your weight goals but also improves your overall physical and mental well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diet is the cornerstone of both weight loss and a healthy lifestyle. It’s not just about what you remove from your plate but what you choose to put on it. A well-balanced diet can boost metabolism, regulate hunger, improve energy levels, and support all aspects of health. When combined with regular physical activity and adequate hydration, the right diet sets the foundation for a better, more vibrant you.
Remember: every healthy choice you make in your diet is a step toward lasting change.

